- March 23, 2023
With Covid vaccination rates increasing and society learning to live with Covid, what will a ‘post Covid’ environment look like and what are the implications for life insurers? In this article, we will review Covid impacts on industry segments, customer life insurance purchasing behaviour and life insurance product definitions – then explore future implications for life insurers.
Industry Segments and Occupational Risk Impacts
Change in employed people and average hours worked, by Industry, February 2020 to August 2021
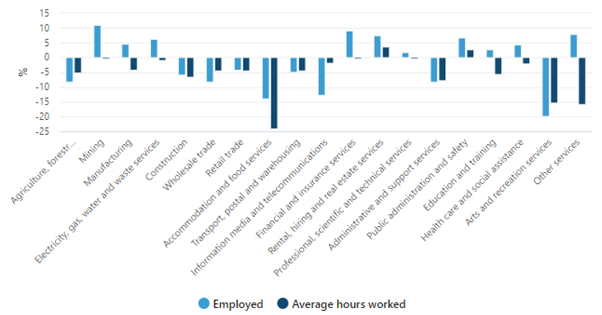
Source: ABS labour force statistics, Australia, Detailed Table 4 and Table 11, taken from https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/charts-casual-employment-occupation-and-industry-august-2021
Covid restrictions have disproportionately affected some industries more than others. ABS labour force statistics suggest “accommodation and food services” and “arts and recreation services” have experienced the largest declines in employment rate and hours worked.
Implications for life insurers:: changes in working arrangements more broadly may have led to shifts in occupation-related risks. Leads for further investigation include:
-
IP incidence and termination rates by industry: is there evidence of worsening experience from specific industries? Is there correlation between job instability and return to work rates?
-
Mental health claims: declining mental health has been widely reported in society. Are some industries more susceptible to mental health claims compared to others? Are there aggravating factors experienced by certain industries (eg income instability, working from home, etc)?
-
Accident claims: what impact has lockdown and increased work from home had on accident rates? Will accident claims return to similar levels once lockdown is over?
-
Industry sector risk ratings: for the purpose of group insurance, Industry sector rating adjustments may provide an important contribution to risk discernment, alongside the traditional approach of occupational category ratings.
Customer Life Insurance Purchasing and Retention Behaviour
Pandemics naturally bring attention to the importance of health. Similarly, the popularity of life insurance is likely to have increased during the period, particularly with broad media coverage of the negative impacts of Covid. How can changes in consumer behaviour due to the pandemic be attributed to changes in new business volumes and reduced lapses?
Diagram: select factors influencing customer purchase or lapse behaviour during Covid
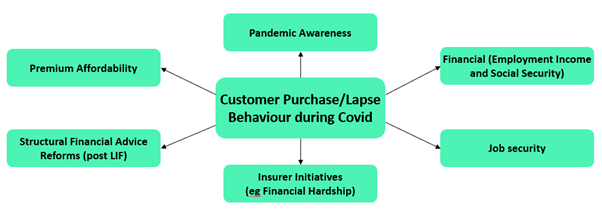
Implications for life insurers: to what degree have new business and lapse volumes been influenced by Covid over the period? Some considerations include:
-
Pandemic awareness & insurer initiatives (eg financial hardship): to what extent has Covid awareness increased new business volumes and insurer financial hardship assistance reduced lapses?
-
Financial & job security: affordability of life insurance affected by household income and availability of government payments. Are there any trends in reasons for lapse activity?
-
Structural advisor reforms & premium affordability: with new business volumes seeing a steady decrease over time and lapse experience improving, to what degree have recent new business volumes and lapses been influenced by structural changes?
Product Definition Leniency
In early 2020, the FSC on behalf of Australian life insurers announced Covid related initiatives to assist customers.¹ With many initiatives discontinued in 2021, should life insurers continue Covid related initiatives? With the ‘living with Covid’ scenario looking more likely, what would be the implication of continuing the initiatives?
Table: Covid related initiatives to assist policyholders introduced in 2020
| 1. Covid TPD claims initiative | 2. Covid commitment to frontline healthcare workers | 3. Support options for Covid related financial hardship | |
| Description | Redundancy due to Covid does not restrict TPD claims | No claim declines or premium impacts for frontline workers | Additional support for customers facing financial hardship |
| Potential risk for insurers | Increased TPD claims and anti-selection risk (due to redundancy) | Increased claims due to Covid illness | Reduced premiums and increased claims (from those who remain) |
Implications for life insurers: while life insurers may absorb some short-term impacts, what are the longer term impacts if Covid related initiatives are extended?
-
If claims cost increase due to Covid, short term impacts can be absorbed by insurers, but longer term cost of initiatives will be borne by policyholders through premium increases.
-
Cross-subsidisation of Covid claims, whereby policyholders at a lower risk of Covid related claims will subsidise premiums for those at higher risk of claim. Should all policyholders bear the cost of Covid claims equally or should some policyholders bear more of the burden than others?
-
Shift in occupation ratings: should occupational ratings change based on exposure to Covid? What would be the societally acceptable outcome?
With the initial Covid panic waning, most nations are moving towards a ‘living with Covid’ mindset. However, Covid has had differential impacts on some segments of society and life insurers need to carefully consider the ramifications of any Covid-related decisions made.
Footnote
¹ https://www.fsc.org.au/policy/life-insurance/commitments

